
Introduction
In the world of medical coding, precision matters — especially when dealing with metabolic disorders like hypercalcemia. The Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code helps healthcare providers classify patients who have elevated calcium levels in their blood, a condition that can signal anything from mild imbalance to a serious underlying disease.
This article dives into the ins and outs of the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code, explaining when to use it, related diagnosis codes, and the best ways to document and code this condition. If you’re a clinician, coder, or biller, understanding this code will help you improve documentation accuracy and streamlinea insurance claims.
What is Hypercalcemia? A Quick Overview
Hypercalcemia is a condition where calcium levels in the blood rise above the normal range—typically higher than 10.5 mg/dL. Calcium is essential for several body processes, including:
- Bone strength and structure
- Muscle contraction
- Nerve impulse transmission
- Blood clotting
Excessive calcium levels can result in a number of symptoms, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Confusion or mental fog
- Nausea and vomiting
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Kidney stones
- Cardiac arrhythmias in severe cases
Because hypercalcemia can indicate anything from a benign cause to a life-threatening illness, accurate diagnosis and documentation are critical — and that starts with proper use of the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code.
The Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code: What You Need to Know
The specific ICD-10 code for hypercalcemia is E83.52. This code is categorized as “Disorders of mineral metabolism” and serves as the standard method for indicating elevated calcium levels when a specific underlying cause has not been established.
Important Information Regarding the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code (E83.52):
- It is a billable code, meaning it can be used on insurance claims.
- It applies when hypercalcemia is documented but the cause is unknown, unspecified, or not recorded.
- It corresponds to the older ICD-9 code 275.42.
- It should be used only when the diagnosis of hypercalcemia is clinically confirmed, typically by lab tests showing elevated serum calcium.
- If the cause of hypercalcemia is known, this code is often secondary to the primary diagnosis.
Using the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code correctly helps distinguish primary metabolic conditions from secondary manifestations.
When to Use the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code (E83.52)
Knowing when to apply E83.52 is key to proper coding. Use this code when:
- The patient has laboratory-confirmed elevated calcium levels.
- The healthcare provider has not identified or documented an underlying cause.
- You want to specifically highlight hypercalcemia as a diagnosis without a linked etiology.
Important:
If the hypercalcemia is caused by another condition, such as cancer or hyperparathyroidism, code the underlying cause first and add E83.52 as a secondary or manifestation code, if relevant. In this context, using the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code as an additional diagnosis ensures that the metabolic aspect is not overlooked.
Common Causes of Hypercalcemia and Related ICD-10 Codes
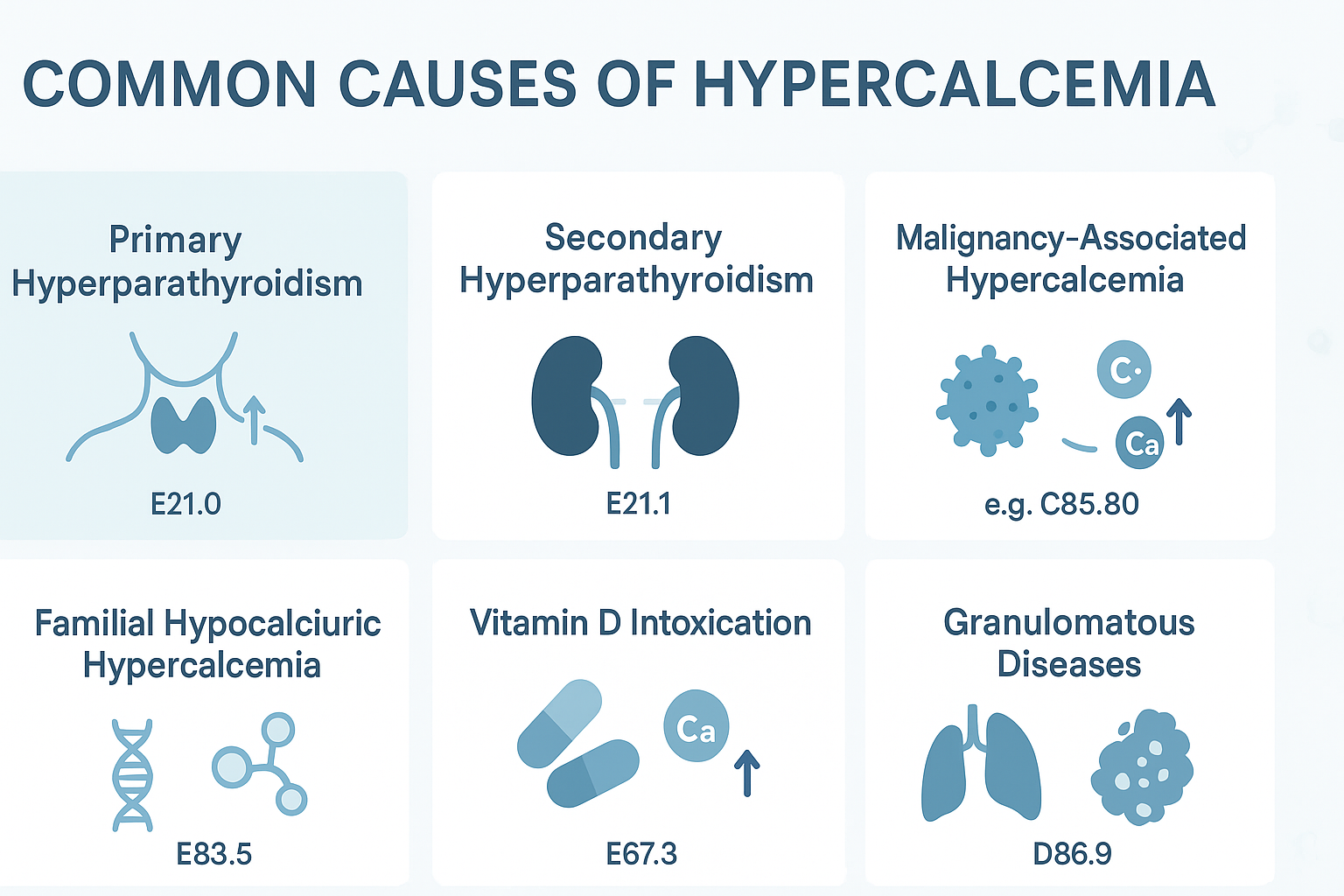
Hypercalcemia can arise from many different causes. Below are some common ones, along with their related ICD-10 codes:
1. Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- ICD-10 Code: E21.0
Blood calcium levels rise as a result of an overactive parathyroid gland producing too much parathyroid hormone. If this is the cause, you should code E21.0 first. If hypercalcemia is being treated particularly, you can also add E83.52.
2. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
- ICD-10 Code: E21.1
This form often results from chronic kidney disease or vitamin D deficiency. Similar coding rules apply: code the cause first, then hypercalcemia.
3. Malignancy-Associated Hypercalcemia
- Example: Lymphoma — ICD-10 Code: C85.80
Cancer can cause hypercalcemia through bone destruction or hormone-like substances secreted by tumors. Before adding E83.52 to indicate hypercalcemia, make sure to code for the cancer.
4. Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (FHH)
- ICD-10 Code: E83.5
This is a rare, inherited disorder causing mildly elevated calcium levels. It’s crucial to distinguish this from E83.52; ensure that you use E83.5 for FHH instead. The Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code is not appropriate for FHH cases.
Best Practices for Coding Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code
To ensure accurate and compliant coding, follow these guidelines:
1. Confirm Diagnosis with Lab Results
Verify elevated calcium levels through lab reports, preferably using corrected serum calcium or ionized calcium values, to account for serum albumin levels.
2. Document the Underlying Cause When Known
If hypercalcemia is due to a disease like cancer or parathyroid disorder, clearly document the cause in the medical record.
3. Sequence Codes Properly
The underlying condition causing hypercalcemia should be coded as the primary diagnosis. Hypercalcemia (E83.52) can then be listed as a secondary or additional diagnosis.
4. Use Specific Terminology
In clinical notes, use terms such as “hypercalcemia secondary to…” or “manifested by hypercalcemia” to clarify the causal relationship.
5. Avoid Misuse of Codes
Do not use E83.52 for genetic conditions like FHH; instead, use E83.5. Also, do not code hypercalcemia without lab confirmation. Proper usage of the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code helps maintain billing integrity and avoids claim denials.
Why Does Accurate Coding of Hypercalcemia Matter?

Proper coding of hypercalcemia affects many aspects of healthcare:
- Improved Clinical Communication: Other providers can understand the patient’s metabolic status and underlying risks.
- Insurance Reimbursement: Accurate codes prevent claim denials and delays.
- Epidemiological Tracking: Health agencies use ICD codes to monitor disease patterns.
- Patient Safety: Ensures the condition is recognized and monitored appropriately.
Using the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code appropriately supports all these benefits and maintains regulatory compliance.
Illustrative Clinical Scenarios
Scenario 1: Hypercalcemia with No Known Cause
A patient’s blood test shows calcium of 11.5 mg/dL. The cause has not yet been determined.
Coding: Use E83.52 — this is the correct Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code for unspecified cause.
Scenario 2: Hypercalcemia Due to Parathyroid Adenoma
A patient has primary hyperparathyroidism causing hypercalcemia.
Coding: Use E21.0 for the parathyroid adenoma and add E83.52 if hypercalcemia is treated as a separate diagnosis.
Scenario 3: Hypercalcemia Secondary to Lymphoma
A patient with lymphoma develops hypercalcemia.
Coding: After applying C85.80 for lymphoma, code E83.52 to be used for hypercalcemia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the exact ICD-10 code for hypercalcemia?
A: The code is E83.52, also known as the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code.
Q2: Can I code hypercalcemia without knowing the cause?
A: Yes, use E83.52 when hypercalcemia is documented but the cause is unknown or not specified.
Q3: Should hypercalcemia always be coded with the primary cause?
A: Yes, if the cause is documented, it should be coded first.
Q4: Is familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia coded as E83.52?
A: No, FHH uses E83.5 — not the standard Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code.
Q5: How important is lab confirmation for hypercalcemia coding?
A: Very important. Always confirm elevated calcium levels before coding.
Q6: Can hypercalcemia be a standalone diagnosis?
A: Yes, but only if no underlying cause is documented.
Summary: Key Takeaways on the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code

- The Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code is E83.52.
- Use it for hypercalcemia without a known or documented cause.
- Code underlying conditions first when known (like hyperparathyroidism or cancer).
- Common causes are represented by related codes such as E21.0 and C85.80.
- Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia is coded with E83.5, not E83.52.
- Accurate coding depends on proper lab results and documentation.
- Clear sequencing and terminology in documentation improve claim acceptance.
Conclusion
Understanding and applying the Hypercalcemia ICD 10 Code correctly is essential for clinicians and coders. It ensures that patients receive proper diagnosis, treatment, and insurance coverage. The code E83.52 serves as a key tool when the cause of elevated calcium isn’t clear, but when the cause is known, related ICD-10 codes take priority.
